Feature Flag Targeting
Targeting Attributes
Feature values can be targeted to specific users or groups of users. In order for this to work, you must pass targeting attributes into the GrowthBook SDK and also list them in the GrowthBook App.
This is an example of specifying the targeting attributes in the SDK:
growthbook.setAttributes({
id: user.id,
email: user.email,
country: user.country,
url: window.location.href,
userAgent: navigator.userAgent,
admin: user.isAdmin,
age: user.age,
});
You can update the attributes in the GrowthBook App under SDK Connections > Attributes:
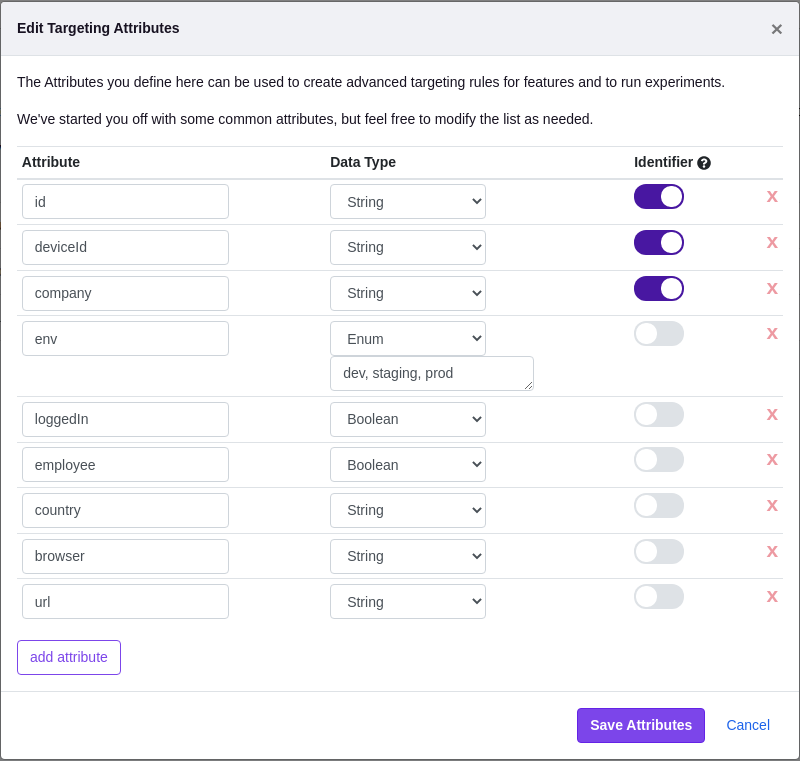
The actual values of the targeting attributes (e.g. the user ids, emails, etc.) are never sent to GrowthBook. They are only stored in memory locally within the SDK. This architecture eliminates huge potential security holes and keeps your user's PII safe and secure.
Each attribute has 3 parts:
- The attribute name itself. This is how the attribute will be referenced in the SDK.
- The data type of the attribute
- Whether it's an identifier. Identifiers are attributes which uniquely identify something - typically either a person, account, company, or device- and are used for experiment assignments.
Attribute Data Types
GrowthBook supports the following attribute data types:
- Boolean - true or false
- Number - Floats or integers
- String - freeform text
- Enum - When there are only a small list of pre-defined values it could take
- Secure String - Like a string, but the values will be hashed before passing to the SDK
- Array of Strings - useful for things like "tags"
- Array of Numbers - useful anytime you have multiple numeric values
- Array of Secure Strings - an array of secure strings useful for passing multiple values that you want to keep secure
Saved Groups
Available via API or under SDK Configuration -> Saved Groups, Saved Groups allows you to define a list of attribute values that can be referenced from feature targeting rules. Saved Group values are passed by reference, so updates will affect all references of this group used in your feature flag targeting rules. Each saved group specifies an attribute for which these are possible values. When targeting to attributes that have a Saved Group defined, you will have options 'Is in the Saved Group' and 'Is not in the Saved Group', and then you can select the Saved Group name. Saved groups are useful to avoid having to copy and paste lists of user attribute values between feature targeting conditions.
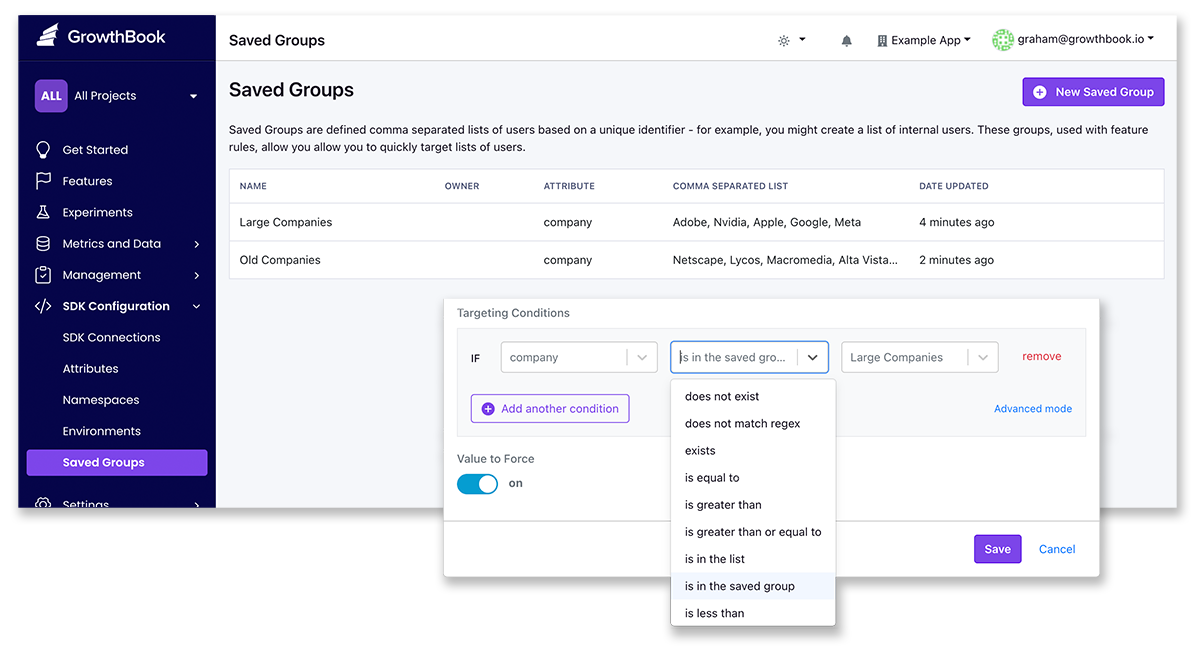
For example, you could make a Saved Group called “Enterprise Customer Ids” that is an array of secure strings, and use it to release all of your new enterprise features. If you later add or remove a customer from the group, it will automatically update all the features.